Safe Mode is a special startup mode in Windows; in this mode, the system loads only the most basic drivers and system services, helping users troubleshoot issues like blue screens and driver conflicts.
Differences between Safe Mode and Normal Mode:
| Item | Normal Mode | Safe Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Drivers Loaded | Loads all drivers | Loads only essential drivers |
| Startup Items & Services | Runs all configured startup items and services | Does not run |
| Resolution | Normal resolution | Low resolution |
| Network Support | Normal network access | No network by default (can choose "Safe Mode with Networking") |
| Third-party Software | Can run normally | Most cannot run or are blocked |
Booting into Safe Mode
Method 1: Via System Configuration
Press the shortcut + R to open [Run], enter msconfig and confirm;
Switch to the [Boot] tab, check [Safe boot] under [Boot options], and select [Minimal];
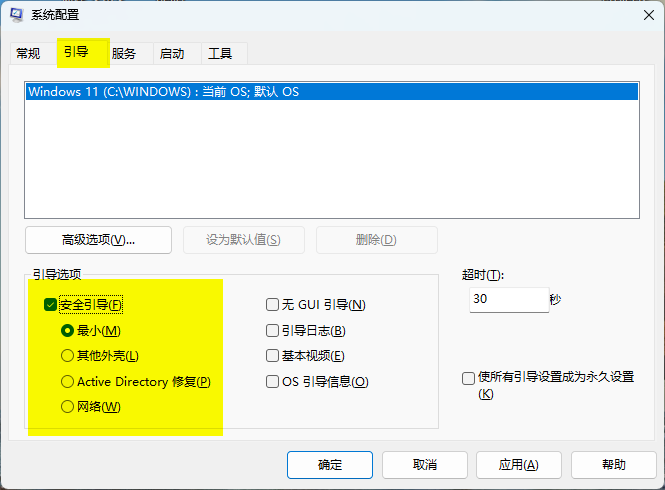
In this mode, network drivers won't be loaded and networking will be unavailable;
To use networking in Safe Mode, select the [Network] option;
Click OK and restart your computer to boot into Safe Mode.
Method 2: Force Trigger Recovery Screen (For systems that can't boot normally)
Interrupt the boot process 3 consecutive times before Windows finishes starting (e.g., by powering off or holding the power button to force shutdown), and Windows will enter recovery mode;
Navigate through: [Troubleshoot] > [Advanced options] > [Startup Settings] > [Restart]
After restarting, select the desired mode:
- Press F4: Boot in Safe Mode
- Press F5: Boot in Safe Mode with Networking
Blue Screen in Safe Mode
This most likely indicates hardware failure or corrupted core system files, requiring hardware inspection or system reinstallation.