A memory dump file is a system memory snapshot that Windows automatically or manually saves when a critical error or application crash occurs; it records the memory state, running processes, drivers, kernel data, and other information at the time of failure for subsequent debugging and root cause analysis.
Collecting Memory Dumps
To configure Windows to create memory dump files during blue screens, follow these steps:
- Type "Advanced system settings" in the taskbar search box and press Enter;

Search for advanced system settings - Under the [Advanced] tab in [System Properties], click the [Settings] button in the [Startup and Recovery] section;
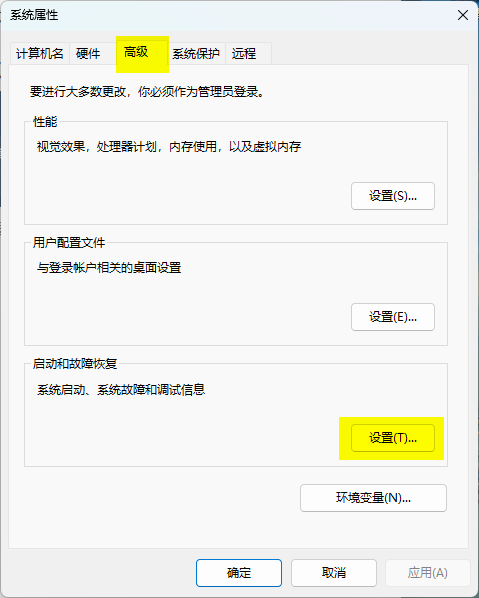
Startup and Recovery - In the new window, select [Small memory dump] from the dropdown under [Write debugging information] and click OK.
%SystemRoot%represents the system directory, typicallyC:\Windows;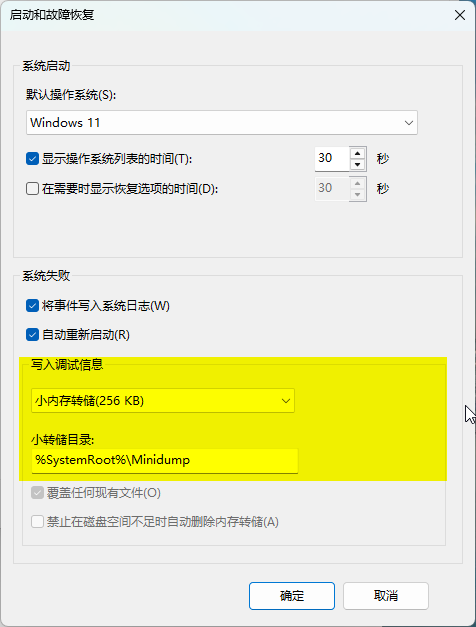
Write debugging information - Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Types of Memory Dumps
| Dump Type | Description | File Size |
|---|---|---|
| Small Memory Dump (256 KB) | Minimal debugging information, suitable for quick diagnosis, containing basic error codes and call stacks. | 256KB |
| Kernel Memory Dump | Contains kernel-mode memory and driver information, excluding user process data. | Typically several hundred MB |
| Complete Memory Dump | Contains the entire contents of physical memory | Equal to system physical memory size |
| Automatic Memory Dump | One of Windows' default settings, automatically adjusts size based on system memory. | Same as Kernel Memory Dump |
| Active Memory Dump | Similar to full dump but excludes unimportant memory pages to reduce size. | Smaller than complete dump |
For general blue screen analysis, use Small Memory Dump; for in-depth analysis, use Kernel Memory Dump or Complete Memory Dump.
Memory Dump Generation Failure
- Verify the dump file save path is correctly configured
- Ensure there is sufficient space to save the file
During a blue screen, a progress bar shows the memory dump progress. If it stays at 0% with error code WHEA-UNCORRECTABLE-ERROR, it's likely caused by hard disk failure. Try reseating the hard drive, changing the interface, or replacing the hard drive.