A system restore point is a snapshot created by the Windows system that records the state of system files, system configuration, registry, drivers, and software at a specific point in time; creating a restore point before making critical changes to the system allows you to roll back to that point if problems occur.
System restore does not affect personal data.
It's recommended to create a restore point before any operation that affects system core components, drivers, registry, or critical configuration; this way, if issues arise, you can restore the system within minutes instead of reinstalling.
Creating a System Restore Point
The system automatically creates restore points during automatic updates!
Press + S, search for "Create a restore point," and click to open;
Or navigate through [Settings] → [System] → [System info] → [System protection];
In the [System Properties] window under the [System Protection] tab, ensure the system drive protection status is enabled under [Protection Settings]; if not enabled, select the system drive, click [Configure], and choose [Turn on system protection];
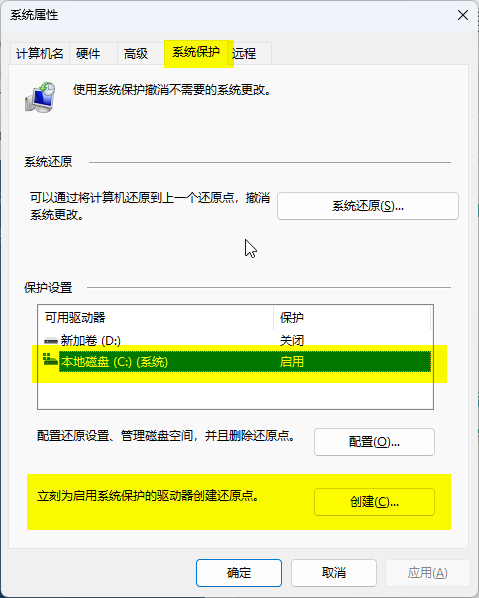
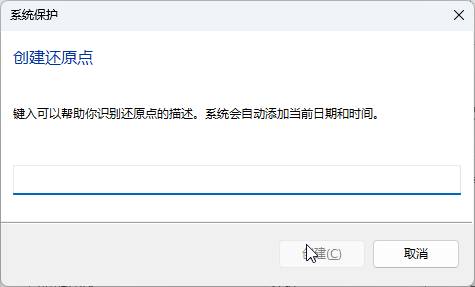
Click the [Create] button, enter a description, then click [Create] again;
Restoring from a Restore Point
When system operations (such as installing drivers or modifying the registry) cause system failures, you can restore the system using a restore point;
In the [System Protection] tab mentioned above, click [System Restore] and select a restore point to recover.