Your network does not support IPv6
Your current network is accessing this website using IPv4.
Your IPv4 address is: 216.73.216.130
Possible Causes
- IPv6 is not enabled or configured correctly; you may need How to Enable IPv6 on Windows
- Using a VPN that does not support IPv6;
You can use this tool to test online whether IPv6 is enabled and quickly query your IPv6 address. If the detection result shows that your network supports IPv6 and displays your IPv6 address, it indicates you are currently accessing this site via the IPv6 protocol.
What is IPv6
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the sixth version of the Internet Protocol, used to assign unique IP addresses to devices on a network. An IP address is the identifier for devices such as computers and mobile phones when communicating over the internet. The main purpose of IPv6 is to address the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses (the previous generation internet protocol) while providing better network performance and security.
Using Commands to Query IPv6 Address
You can open the Windows terminal and enter the command ipconfig to query IPv6 address information.
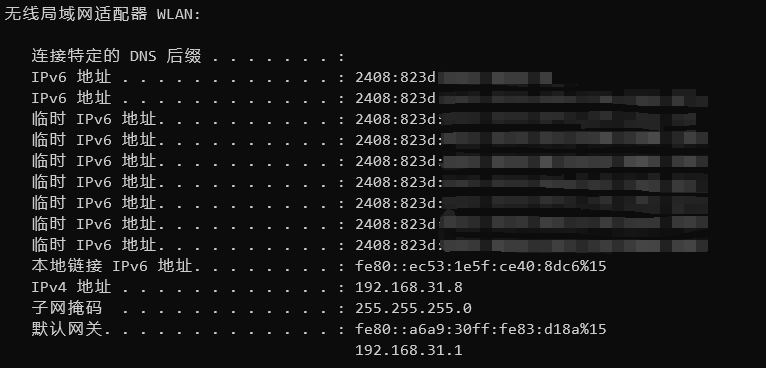
You may see multiple IPv6 addresses. In the image:
- The first IPv6 address: Assigned by DHCP.
- The second IPv6 address: The real IPv6 address.
- Temporary IPv6 address: There may be multiple. Temporary IPv6 addresses are dynamically generated IP addresses in the Windows system to enhance user privacy and security. When a Windows device connects to a network, temporary addresses are periodically changed to avoid tracking and identification.
Typically, when accessing the network, temporary IPv6 addresses are used.
You may need:
IPv6 Address Format
An IPv6 address consists of 8 groups of hexadecimal numbers, each group containing 4 hexadecimal digits. The format is as follows:
xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx
Where each xxxx ranges from 0000 to FFFF.
To reduce redundancy, IPv6 addresses allow several simplified representations:
- Leading zeros can be omitted: Leading zeros in each group can be dropped.
- Consecutive zeros can be abbreviated as
::: A consecutive block of zero groups can be abbreviated as a double colon::, but this can only be used once.